

The equation for the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient, r, is: If known_y's and known_x's contain only 1 data point, RSQ returns the #DIV/0! error value. If known_y's and known_x's are empty or have a different number of data points, RSQ returns the #N/A error value.
If an array or reference argument contains text, logical values, or empty cells, those values are ignored however, cells with the value zero are included.Īrguments that are error values or text that cannot be translated into numbers cause errors. Logical values and text representations of numbers that you type directly into the list of arguments are counted. An array or range of data points.Īrguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers. The RSQ function syntax has the following arguments: The r-squared value can be interpreted as the proportion of the variance in y attributable to the variance in x. For more information, see the PEARSON function. Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient through data points in known_y's and known_x's. This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the RSQ
#INTERPRET REGRESSION EXCEL FOR MAC FOR MAC#
QI Macros can also perform Multiple Regression Analysis.Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More. This provides you with information on how the confidence level can impact your results, depending on where alpha is set. The 95% and 99% Confidence Levels reference when your alpha value is set at. Please note that the straight lines found in your first chart (Salt concentration) represent the Upper and Lower Prediction Intervals, while the more curved lines are the Upper and Lower Confidence IntervalsĬonfidence Intervals provide a view into the uncertainty when estimating the mean, while Prediction Intervals account for variation in the Y values around the mean.

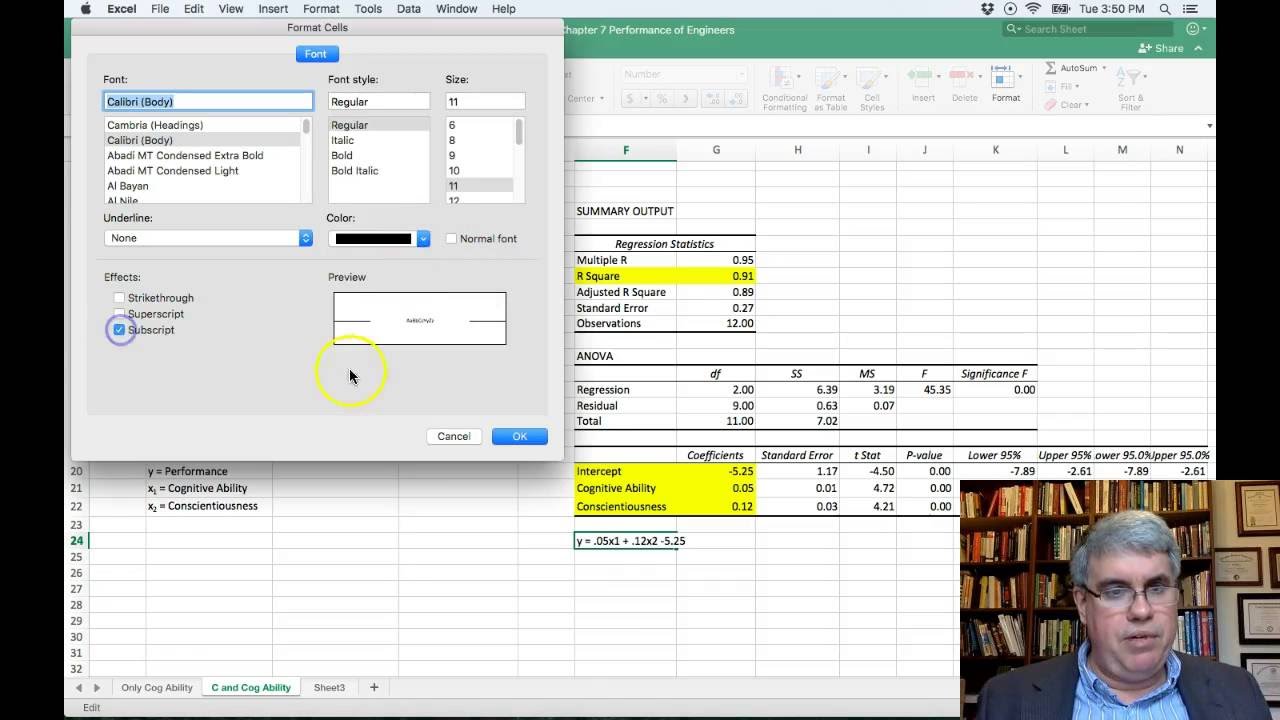
In addition to the Summary Output above, QI Macros also calculates Residuals and Probability Data and creates scatter plots in Excel for you: Residuals Output, Probability Output and Charts For example, if the % of paved roadway = 1% the Salt concentration could be estimated as 17.547* (1%) +2.6765 = 20.2235 mg/l. Using the equation, y = Salt concentration = 2.677 + 17.547*(% paved roadway area), you could predict the salt concentration based on the percent of paved roadway. Use the Equation for Prediction and Estimation In other words, there is a relation between the two variables. Since the p value ( 0 < 0.05), we reject the null hypothesis that the two variables are unrelated. 951 means that 95.1% of the variation in salt concentration can be explained by roadway area. Some statistics references recommend using the Adjusted R Square value. QI Macros will perform the regression analysis calculations for you:Īnalysis: If R Square is greater than 0.80, as it is in this case, there is a good fit to the data.Click and drag over your data to select it and then click on QI Macros, Statistical Tools and Regression:.Enter your data into Excel with the independent variable in the left column and the dependent variable in the right column.This sample data is found in QI Macros Test Data > statistical.xlsx > Regression Data: What if we wanted to know if the salt concentration in runoff (dependent variable) is related to the percent of paved roadway area (independent variable). Regression arrives at an equation to predict performance based on each of the inputs. The purpose of regression analysis is to evaluate the effects of one or more independent variables on a single dependent variable. Statistical Analysis Excel » Regression Analysis Regression Analysis in Excel You Don't Have to be a Statistician to Run Regression Analysis


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
